Contact sports, while exhilarating and rewarding, carry significant risks, particularly concerning injuries to the spine. Among these injuries, compressed spine injuries can have profound long-term effects on athletes. Understanding these consequences is crucial for athletes, coaches, and healthcare professionals alike. This article delves into the nature of compressed spine injuries, their immediate and long-term impacts, and the importance of proper rehabilitation and treatment.
Understanding Compressed Spine Injuries
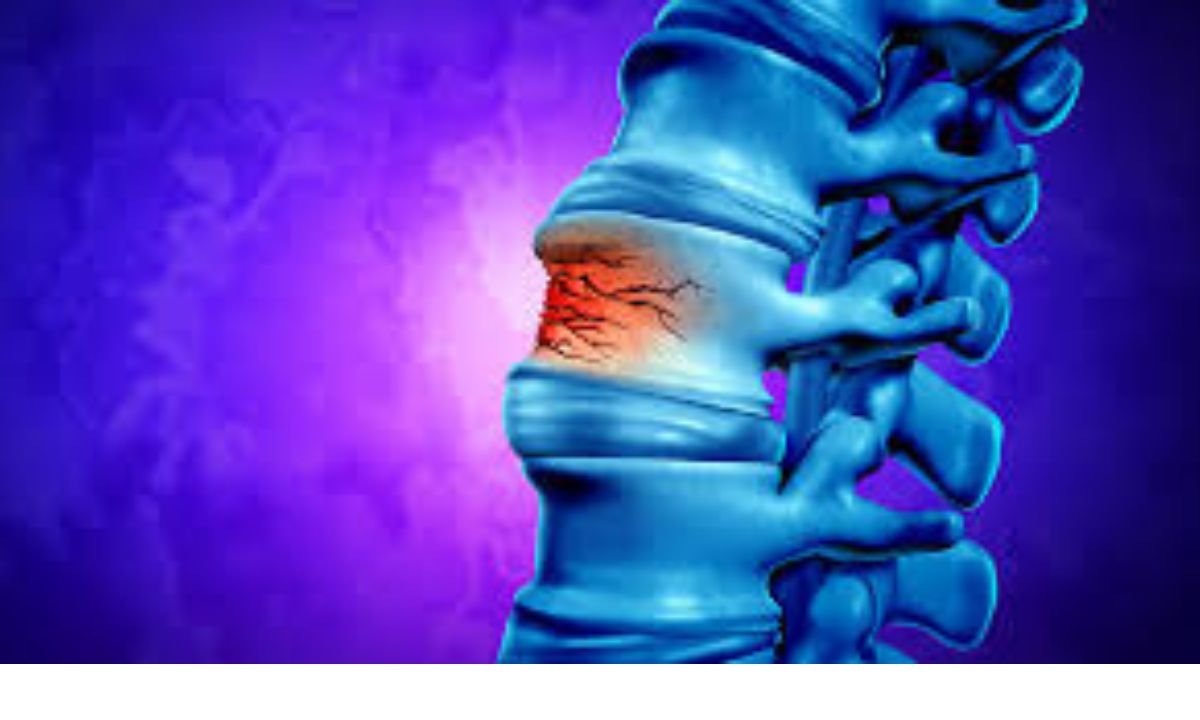
Compressed spine injuries occur when excessive force compresses the vertebrae, leading to conditions like fractures, disc herniation, or spinal stenosis. In the final stages of spinal stenosis, the spinal canal narrows significantly, which can lead to severe nerve compression. This may result in debilitating pain, weakness, and numbness in the extremities, affecting an individual’s mobility and quality of life.
These injuries can disrupt the normal alignment and function of the spine, potentially affecting the surrounding nerves and tissues. In athletes, particularly those engaged in contact sports, these injuries can result from high-impact collisions, falls, or repetitive stress on the spine. The accumulation of such trauma can exacerbate the progression of spinal stenosis, underscoring the importance of injury prevention and proper treatment.
Common Causes of Compressed Spine Injuries in Contact Sports
The nature of contact sports inherently exposes athletes to risks of spinal injury. Common causes include:
- Tackling and Blocking: In sports like football, the act of tackling can place immense pressure on the spine.
- Falls: Athletes can suffer significant impacts from falls during play, which can lead to compression.
- Repetitive Strain: Activities that involve repetitive twisting or bending can contribute to cumulative spinal injuries over time.
Understanding these causes is essential for developing effective prevention strategies.
Immediate Effects of Compressed Spine Injuries
The immediate effects of compressed spine injuries can vary in severity, including:
- Pain: Acute pain in the back or neck is a common symptom, which can be debilitating.
- Numbness or Weakness: Compression of spinal nerves may result in sensations of numbness, tingling, or weakness in the limbs.
- Limited Mobility: Affected athletes may find it challenging to move freely or perform their sports-related activities.
Immediate medical attention is critical to address these symptoms and prevent further damage.
Long-Term Physical Consequences
The long-term physical consequences of compressed spine injuries can be significant and life-altering. These may include:
- Chronic Pain: Many athletes experience ongoing pain that can hinder their ability to engage in physical activity or daily tasks.
- Mobility Issues: Long-term compression may lead to decreased range of motion or even permanent disability.
- Degenerative Conditions: Injuries can accelerate the development of conditions like arthritis or degenerative disc disease, impacting long-term health and quality of life.
According to Dr. Tawfik, a well-known spine doctor in New Jersey, recognizing these potential outcomes underscores the importance of early intervention and ongoing care. Athletes and healthcare providers should prioritize regular assessments and tailored rehabilitation programs to mitigate these long-term consequences effectively. Engaging in proactive treatment strategies can empower athletes to manage their injuries and maintain a better quality of life, allowing them to enjoy their passions both on and off the field.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
The impact of compressed spine injuries extends beyond physical consequences. Athletes may experience:
- Anxiety and Depression: Concerns about recovery, future performance, and chronic pain can lead to mental health challenges.
- Loss of Identity: For many athletes, their sport defines a significant part of their identity, and injuries can lead to feelings of loss or grief.
- Social Isolation: Reduced participation in sports can lead to isolation from teammates and friends, further affecting mental health.
It’s crucial to address these psychological impacts as part of a holistic recovery strategy.
Strategies for Prevention and Management
Preventing compressed spine injuries involves a multifaceted approach:
- Proper Training: Athletes should receive proper training on techniques to minimize the risk of injury.
- Strength and Conditioning: Building core strength can provide better support for the spine.
- Protective Gear: Using appropriate protective equipment can help absorb impacts and reduce the risk of injury.
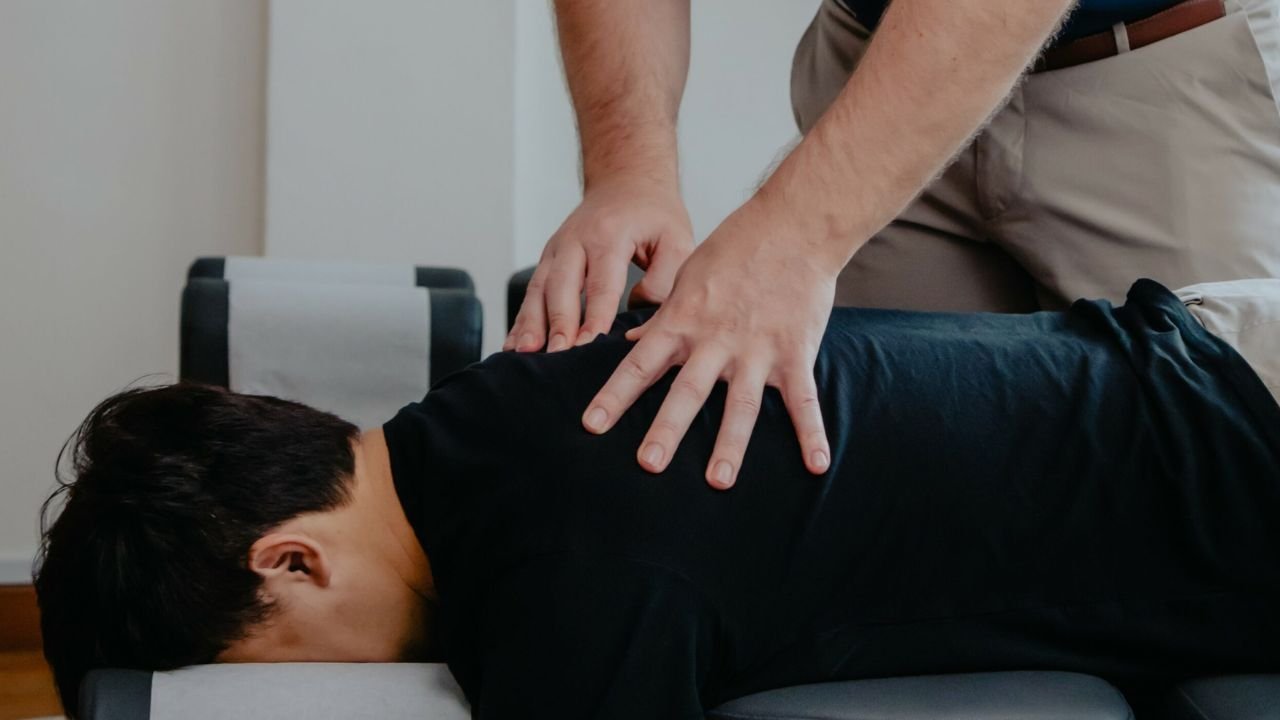
Importance of Rehabilitation and Treatment
Rehabilitation is a critical component of recovery from compressed spine injuries. It involves physical therapy, medication, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Professional rehabilitation and treatment are vital for athletes recovering from compressed spine injuries. The resources available, including skilled spine surgeons and local back doctors, play a crucial role in supporting recovery and ensuring athletes can return to their sport safely.
Conclusion
Understanding the long-term effects of compressed spine injuries in contact sports is essential for athletes and sports professionals. By recognizing the potential physical, psychological, and emotional impacts, and prioritizing prevention and effective rehabilitation, athletes can improve their chances of a successful recovery. Access to specialized care, including spine surgery and ongoing support from back doctors, can make a significant difference in the recovery journey, allowing athletes to return to their passion while maintaining their overall health.